Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-08-04 Origin: Site








 Carbon fiber fabric is made from carbon strands woven together tightly. This makes a material that is light and strong. Many industries use it because it works better than materials like aluminum and steel. Carbon fiber fabric is about 2.3 times stronger than aluminum. It also weighs almost 59% less than aluminum.
Carbon fiber fabric is made from carbon strands woven together tightly. This makes a material that is light and strong. Many industries use it because it works better than materials like aluminum and steel. Carbon fiber fabric is about 2.3 times stronger than aluminum. It also weighs almost 59% less than aluminum.
| Property | Carbon Fiber | Aluminum | Comparison Ratio (Carbon/Aluminum) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | ~1035 | ~450 | ~2.3 times stronger |
| Density (g/cm³) | ~1.6 | ~2.7 | ~59% (lighter) |
| Specific Tensile Strength | ~647 (MPa/(g/cm³)) | ~166 (MPa/(g/cm³)) | ~3.9 times higher |
This special mix of strength and low weight makes it popular. Many industries want to use carbon fiber fabric. The global market for carbon fiber fabric is growing fast, as you can see below:
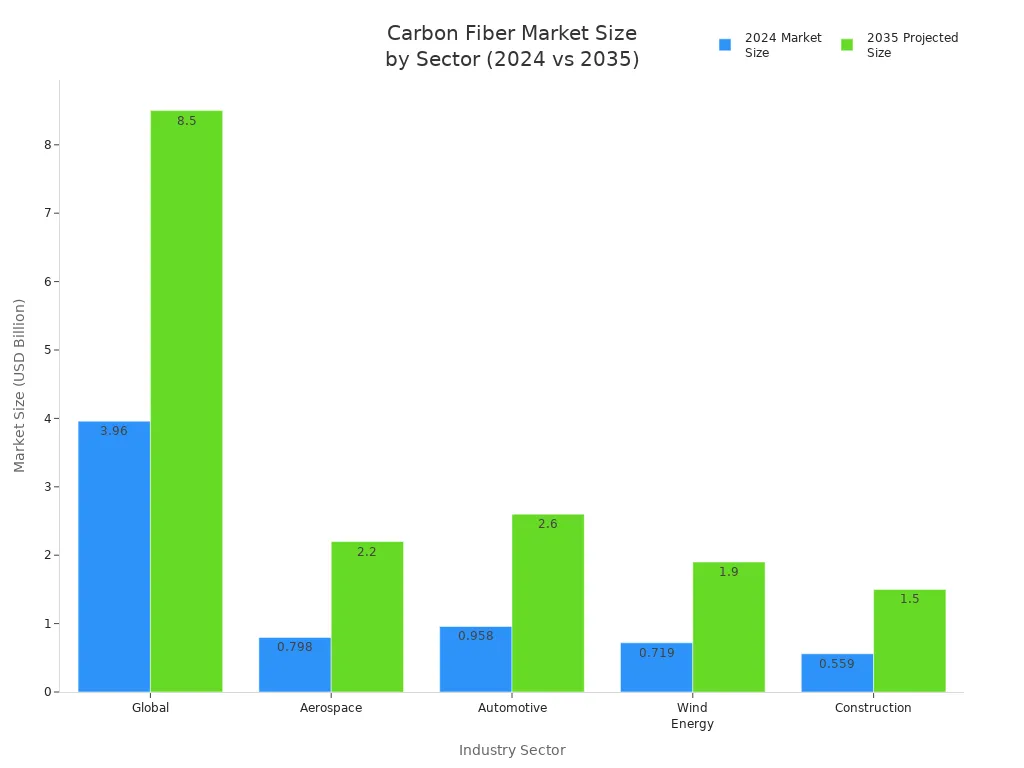
Think about a bike frame that is lighter than aluminum but much stronger—would you pick carbon fiber fabric for your next project?
Carbon fiber fabric is very strong and light. It is better than metals like aluminum and steel for many things.
There are different kinds of carbon fiber fabrics. Some are woven and some are unidirectional. Each type is good for certain strength and shape needs.
Carbon fiber fabric is used in many industries. These include aerospace, automotive, construction, sports, marine, and medical. It lasts a long time and can handle heat and chemicals.
Picking the right carbon fiber fabric depends on what the project needs. You must think about strength, weight, shape, and cost.
Trying small samples and buying from trusted sellers helps you get the best results with carbon fiber fabric.

Carbon fiber fabric is made by weaving thin carbon strands. Each strand has thousands of tiny filaments. These filaments look like a sheet of small threads. The carbon atoms in the threads are tightly bonded. This makes a structure like graphite. This special pattern gives the fabric its light weight and strength. The inside structure can change depending on how it is made. Some types have neat layers stacked together. Others have a more mixed-up pattern. Sometimes, the inside and outside of the fiber are different. This can change how the fabric acts. The way the carbon atoms are set up helps the fabric become strong and stiff. That is why it is used in high-performance composites.
Making carbon fiber fabric takes several steps. Each step changes how the material will turn out. Here is a simple list of how it is made:
Pick raw materials, usually polyacrylonitrile or pitch-based precursors.
Spin the precursor into thin fibers.
Heat the fibers in air at 200 to 300°C to stabilize them.
Heat the fibers in a special gas at 1000 to 3000°C to carbonize them. This step removes other elements and adds more carbon.
Treat the fiber surface to help it stick to resins.
Add sizing to protect the fibers and make them easier to use.
Weave the finished fibers into fabric.
How the polymer chains line up in the fibers is important. When they line up well, the fabric gets stronger and stiffer. Heating the fibers removes things that are not carbon. It also helps the carbon atoms form neat layers. Each step must be done carefully to avoid mistakes. This helps the fabric reach its best strength. The last step is weaving, which makes the patterns you see in carbon fiber fabric.
Woven carbon fiber is special because of its great features. It is light but also very strong and stiff. The table below shows how carbon fiber compares to other materials:
| Material | Elastic Modulus (Stiffness) | Ultimate Tensile Strength | Density (Weight) | Stiffness-to-Weight Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Fiber (fiber) | 33 msi (228 GPa) | 500 ksi (3.5 GPa) | N/A | N/A |
| Carbon Fiber Composite (typical) | ~10 msi | ~90 ksi | ~0.05 lbs./in⊃3; | 160 x 10⁶ |
| Plain-Weave Carbon Fiber Composite | 8 msi | N/A | 0.05 lbs./in⊃3; | 160 x 10⁶ |
| 6061-T6 Aluminum | 10 msi | 65 ksi | 0.10 lbs./in⊃3; | 100 x 10⁶ |
| Steel (4130) | 30 msi | 125 ksi | 0.30 lbs./in⊃3; | 100 x 10⁶ |
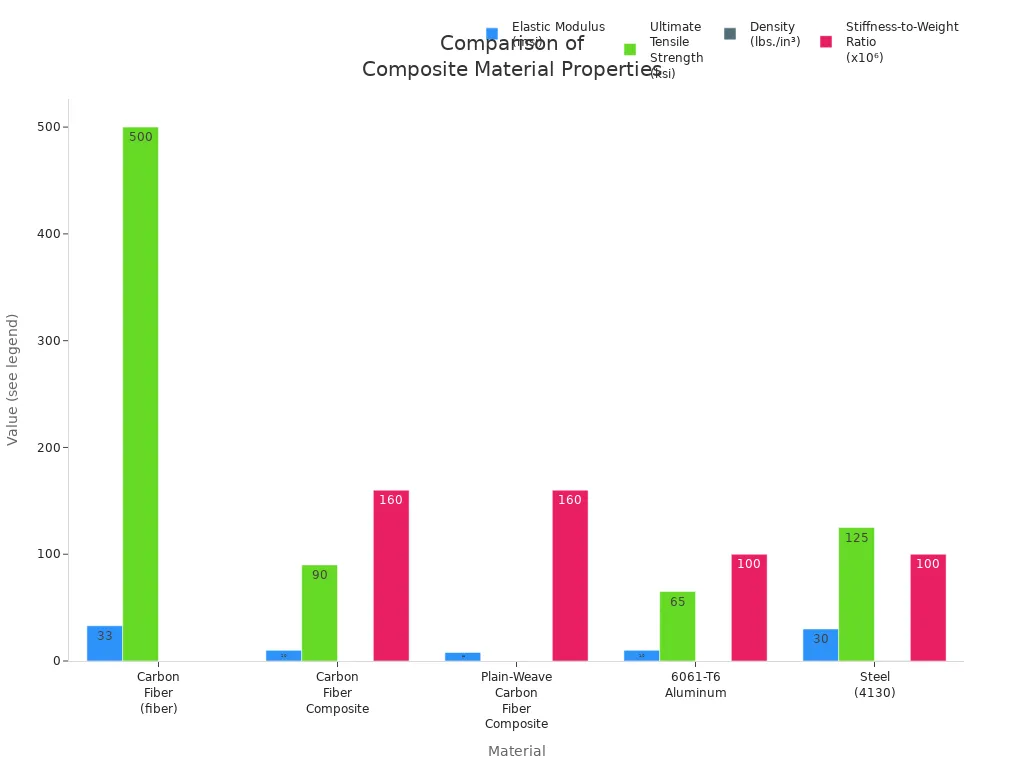
Woven carbon fiber has a much better stiffness-to-weight ratio than aluminum or steel. This means it can hold heavy things but does not weigh much. Carbon fiber fabric is very strong and does not break easily. It can also handle heat and chemicals well. Woven carbon fiber can carry electricity and heat, especially with a metal coating. This is helpful when both strength and conductivity are needed. The special mix of properties lets engineers make lighter, stronger, and longer-lasting composites than older materials.
Woven carbon fiber fabrics have fibers that cross in two ways. These ways are called warp and weft. The fibers go over and under each other. This makes a sheet that is strong and steady. Woven carbon fiber has strength in both directions. It works well for parts that face force from many sides. The weaving makes the fabric thicker and heavier than some others. Woven carbon fiber can bend to fit around curves and shapes. Engineers use it in planes, cars, and sports gear. It can take hits and spread out stress.
Woven carbon fiber fabrics can handle damage better. They work well when parts get hit or cracked.
Unidirectional carbon fiber fabric has all fibers going one way. This gives the most strength and stiffness in that direction. Unidirectional fabrics are thin and light. They fit well on bumpy surfaces and stick to shapes. Workers can cut them to any size with normal tools. The fabric is much stronger than steel. Its elastic modulus is almost like steel. Unidirectional fabrics are best when force goes one way. They are good for beams or fixing cracks in concrete. Many engineers use them to add strength without changing how things look.
Here is a table that compares woven and unidirectional carbon fiber fabrics:
| Aspect | Woven Carbon Fiber Fabrics | Unidirectional Carbon Fiber Fabrics |
|---|---|---|
| Fiber Orientation | Fibers cross at 0° and 90° (warp and weft) | Fibers all go in one direction |
| Weave Patterns | Plain, twill, satin; changes how it bends | No weave; fibers are straight |
| Strength Distribution | Strength in many ways, less in one way | Very strong in fiber way, weak across |
| Thickness & Weight | Thicker and heavier because of weave | Thinner and lighter, fits bumpy surfaces |
| Drapability | Bends well, fits tricky shapes | Bends less, used for one-way strength |
| Manufacturing Complexity | Weaving is harder and costs more | Easier to make, simple to cut and use |
| Typical Applications | Planes, cars, repairs needing strength in many ways | Used where force is one way |
| Mechanical Properties | Balanced strength and stiffness | High strength and stiffness like steel |
Unidirectional fabrics work best when force goes with the fibers. Woven carbon fiber fabrics give balanced strength and resist hits better.
Woven carbon fiber comes in different patterns. Each pattern changes how the fabric works. The three main patterns are plain, twill, and satin.
| Weave Pattern | Structural Details | Advantages | Limitations | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plain Weave | Over-under pattern, short links, very stable | Very stable, good for flat and simple shapes | Not very bendy, can stress at bends | Flat panels, car parts, plane parts |
| Twill Weave | Over-under with longer floats, diagonal lines | Bends well, flexible, looks nice | Not as stable | Curvy shapes, bike parts, sports gear |
| Satin Weave | Long floats, smooth surface | Bends best, smooth, fits curves well | Not very stable | Fancy car parts, electronics, curved plane parts |
Plain weave looks like a checkerboard. It is strong and steady but not very bendy. Twill weave has slanted lines and bends more, so it wraps shapes better. Satin weave has fewer cross points and feels smooth. It fits around curves and looks shiny. Satin weave is used for shiny or tricky shapes.
Some jobs need special carbon fiber fabrics. Wide flat tow fabric uses wide bundles of fibers. It covers big areas fast and looks smooth. Forged carbon fiber fabric uses chopped fibers mixed with resin. This makes parts with random fiber patterns. Forged carbon fiber fabric is strong and looks different. Engineers pick special fabrics for odd shapes, quick work, or a special look. These choices help solve hard problems in cars, planes, and sports gear.
Tip: Pick the right carbon fiber fabric for the shape, strength, and look you want.

The aerospace industry uses carbon fiber fabric the most. In 2024, it has over 32% of the market. Engineers put carbon fiber in wings and fuselages. They also use it for engine cowlings, helicopter blades, and satellites. These parts are strong and light. Planes with carbon fiber parts weigh less. This means they use less fuel and can carry more cargo. Carbon fiber does not rust or get tired easily. This helps planes last longer and stay safe. The smooth surface helps planes move through air better. This makes flights use less energy.
Car makers use carbon fiber to make cars lighter and stronger. They put it in body panels, chassis, and suspension parts. Carbon fiber parts lower the car’s weight. This helps cars use less gas and pollute less. Electric cars do better with carbon fiber. Lighter frames help balance heavy batteries. This lets electric cars go farther. Carbon fiber is strong, so cars can be thin and still safe. It does not rust, so cars last longer and need less fixing.
Builders use carbon fiber fabric to fix and strengthen bridges and buildings. Workers put carbon fiber sheets on beams, columns, and arches. This makes concrete stronger and more bendy. It does not add much weight or change how things look. Carbon fiber bends to fit many shapes. It does not rust, so it protects buildings from bad weather. Putting it on is fast and does not need big machines. This saves money and time.
Carbon fiber fabric has changed sports gear a lot. Makers use it for bike frames, golf clubs, tennis rackets, and skis. The light weight helps athletes move faster and control better. Its strength and stiffness help gear take hits and last longer. Carbon fiber lets makers design gear for each athlete. Lighter and stronger gear helps players do better and stay safe.
| Benefit | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Lightweight Design | Sports gear is lighter, so athletes move faster and easier. |
| Superior Strength & Stiffness | Gear takes hits better, gives more control, and keeps athletes safe. |
| Enhanced Durability | Equipment lasts longer, even when used a lot. |
| Shock Absorption | Carbon fiber spreads out hits, so athletes are protected. |
Boat builders use carbon fiber fabric for hulls and masts. It does not rust in saltwater and stays strong for years. The light weight helps boats go faster and use less fuel. In medicine, carbon fiber is strong and safe for the body. Doctors use it for prosthetics, tools, and implants. It does not block X-rays or MRIs, so doctors see clearly. Patients get lighter, comfy devices that last and work well.
Carbon fiber fabric helps many industries, like aerospace, cars, sports, building, boats, and medicine.
Picking the right carbon fiber fabric starts with knowing your project. Engineers think about what the part will do and how much force it will get. They also look at where the part will be used. Car and airplane parts must be strong and last a long time. The place where the part goes is important too. Some parts need to stand up to water, chemicals, or sunlight. Carbon fiber fabric is good for tough places. It does not rust and can handle hot or cold weather.
Here are some steps for picking carbon fiber fabric: 1. Decide what the part will do, how big it is, and how long it should last. 2. Think about if the part needs to bend or just be very strong. 3. Choose a weave that fits the job, like plain for looks or twill for strength. 4. Make sure the fabric can take the weather and heat it will face. 5. Use carbon fiber sheets with rods or tubes if you need more support.
Tip: Try out a small piece before using a new fabric for the whole project.
Carbon fiber composites are strong but not heavy. This is called a high strength-to-weight ratio. Carbon fiber fabric is lighter than metals like steel or aluminum. In planes, engineers use thin fabrics to keep weight low. Cars and sports gear may use thicker fabrics for more strength. The number of layers changes how strong and heavy the part is. More layers make it stronger but harder to shape.
| Application | Typical Thickness | Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | 0.05–0.2 mm | Lightweight, strong |
| Automotive | 0.15–0.35 mm | Stiffness, safety |
| Sports Gear | 0.15–0.35 mm | Durability, control |
Cost is important when picking carbon fiber fabric. The price depends on what it is made from, how thick it is, and the weave type. Thicker and special weaves cost more money. Woven carbon fiber fabric usually costs $25 to $45 per square meter. How you make the part, like wet layup or vacuum infusion, also changes the price. Prices can go up or down with supply, demand, or new technology. Engineers must pick fabric that works well and fits the budget.
Note: Always make sure the resin matches the carbon fiber fabric. This helps the part stay strong and last a long time.
Carbon fiber fabric is strong and light. It can handle heat and chemicals well.
People use it in planes, cars, sports gear, and fixing buildings. It works well and lasts a long time.
Picking the right kind is important for every job.
Experts and sellers help you choose the best fabric and check quality.
If you are new, you can try small projects first. Follow easy steps and safety rules.
You can find help from good sellers and online guides if you need more advice.
Carbon fiber fabric has carbon atoms packed close together. This makes it very strong and stiff. Steel is much heavier for the same size. It is also not as stiff as carbon fiber. Engineers pick carbon fiber when they want strong and light parts.
Yes, carbon fiber fabric can handle heat and many chemicals. It keeps its shape and strength in hard places. That is why it is used in planes, cars, and buildings.
Workers use sharp scissors or special tools to cut it. They wear gloves and masks to stay safe. The fabric bends and wraps around curves before resin is added. This helps make strong parts that fit well.
Doctors use carbon fiber fabric for prosthetics and tools. It does not block X-rays or MRIs. Patients get lighter and more comfortable devices.
Many sellers offer carbon fiber fabric online. Some stores give samples for small projects. People should check if the seller is trusted and read about the product before buying.
